Cyber security is on everyone's lips these days. This domain has gained massive importance in the last couple of years, especially when data breaches are common now. With so many "hackers" the need for specialized cyber cops increased dramatically. Have you ever heard of the dark web? Are you afraid of "the mother"? You should be. This article will expose you to what happened at the beginning of 2024.
We will start by reading an introduction to cybersecurity, and the biggest breaches that appeared. After that, we will go directly to "The Mother". This mother is different from yours. Stay with us till the end, and then change your passwords.
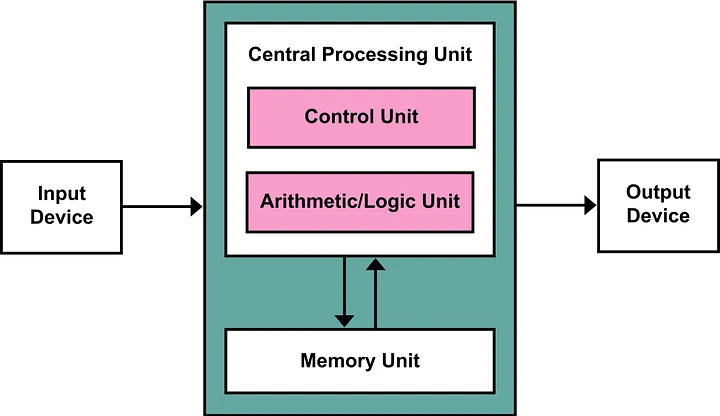
What is cyber security?
Cyber security is the art of protecting (your) computers, mobile devices, networks, and (sensitive) data from attacks.
This domain is responsible for keeping you and your family safe on the internet (and in real life).
Do you remember how viruses were on the web pages 20 years ago? Well, cyber security protects you from those threats and many more. Honestly, it doesn't protect you anymore from that type of threat. Hackers and technology have evolved, so that type of malware has become redundant.
I do not say that it is not possible to gain a virus from whatever random strange website, but it is not probably. Also, in 2024 the focus is on data, and data leaks, not on stealing your MMORPG account.
With everyone going online these days, it is crucial for everyone and every company to have systems that protect you.
Let's conclude that Cyber Security equals the collection of methods used to keep you safe.
The History
Contrary to what the media tells you, this field is not from the last couple of years. It is older than the internet, with a history of over 80 years, by now.
1940s - The time before
The first digital computer was built in 1945. During that time, limited groups of people had access to the enormous electronic machines, which weren't networked. Only a phew knew how to operate them, making cybercrime nonexistent.
Seriously, why would you have any desire to hack this?
Well, let's just ask John von Neumann. He was the one who first raised the theory of computer programs reproducing themselves, back in 1949. This design is arguably the world’s first computer virus but in reality, it is the first concept/design. This concept was proven 22 years later.
1950s - The phone phreaks
Hacking computers for data was not the first purpose for hackers. It might be better to say that phones were the first to get hacked. In the 1950s phone phreaking became popular.
This is a collection of techniques used by "phreaks", to avoid paying long-distance charges. Free calls in the 50s? Well, these "phreaks" had those. And no, you had to pay lots of $ for calls in those years. Free calls & SMSs came way later.
This practice gradually disappeared in the 80s, 30 years later. However, phone providers took a massive hit due to those "phreaks".
1960s - The quiet times
In the 60s, computers remained as massive mainframes kept in temperature-controlled, safe environments. And it was pretty expensive to have one.
During these years, the term "hacking" was in development. It wasn't a big business (yet). There were no opportunities for economic gains. Not even for political ones. It was just about seeing if "you can".
1967 was a really interesting year for cybersecurity history. IBM invited some students to check out a new computer. Those students were first trained on this computer. Afterward, they had access to numerous system components. As a result, IBM learned the system's weaknesses.
It might be possible that this was the first instance of "ethical hacking". These days, being an ethical hacker is a good field, and you can learn it with a certified Ethical Hacker online training.
1970s - ARPANET and the Creeper
The 1970s were crucial for the cybersecurity industry. This period is considered the actual start of it.
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the initial endeavor in this. Before the internet, this connectivity network was created.
The first computer worm "I'm the creeper; catch me if you can!" was created by Bob Thomas, an ARPANET developer. This program could switch from one machine to another by itself.
Getting rid of this worm was a challenge. Ray Tomlinson, an ARPANET researcher created a program called Reaper to find and eliminate this worm. Also, this researcher designed the first networked mail messaging system.
1980s - The birth of Commercial Antivirus
Attacks increased in frequency in the 1980s, including those at National CSS, AT&T, and Los Alamos National Laboratory.
In 1983, the terms "Trojan Horse" and "computer virus" made their appearance. This decade is known as the advancement of computer crime. In the Cold War, the threat of cyber espionage increased.
1987 marked the beginning of commercial antivirus programs, with released titles like Anti4us and Flushot Plus.
1990s - The New Online World
If you are like me, you remember this period. The internet developed in massive proportions during this decade. With this development, the cybersecurity sector expanded. Here are the significant developments in this decade:
Polymorphic viruses - The first code that mutates as it spreads was created in 1990. It was extremely difficult to detect.
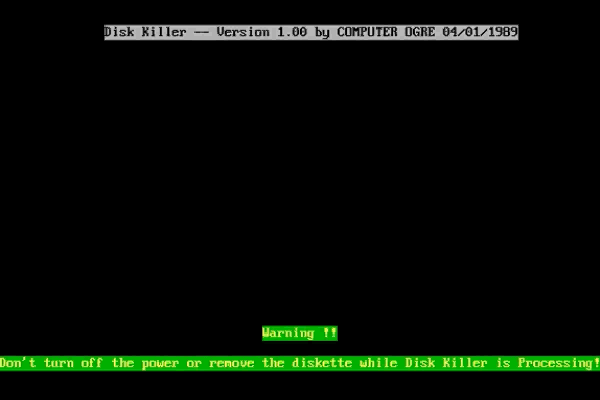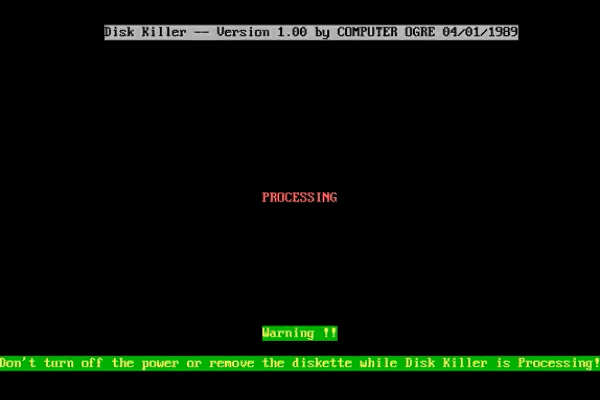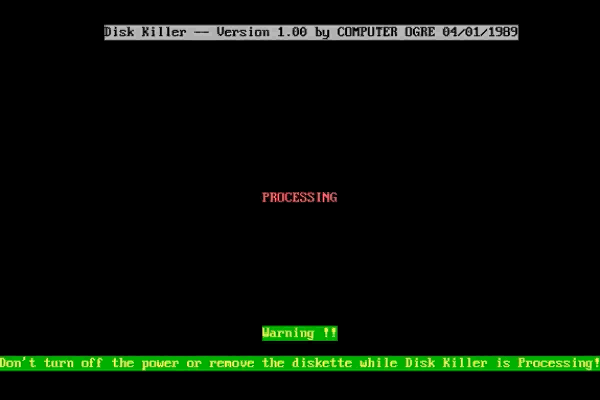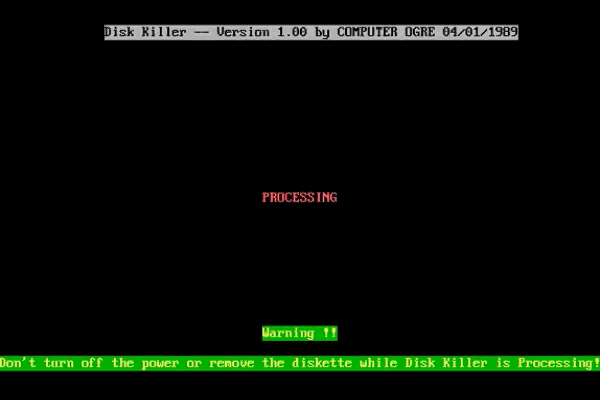
The DiskKiller malware was introduced by PC Today, a magazine for computer users. Numerous PCs were infected, but the company said that it was an accident.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) was introduced in 1995. It helps to secure internet transactions, web browsing, and online data. Netscape developed the protocol for it. it. Later, it would act as the basis for the HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) that we are using today.
The 2000s - The diversification of threats
By this period, most homes and businesses had computers. With this, cybercriminals had even more work to do. They have invented a brand new type of infection: Viruses on websites.
Oh yes, a type of malware that didn't require downloads. This was a real threat. During this period, instant messaging systems were compromised.
In the 2000s, the number of credit card hacks skyrocketed. Massive credit card data leaks took place. Yahoo was one of the main targets for hackers.
Yahoo accounts of over 3 billion users were in the hacker's hands.
The Biggest Moments In Cyber Security Recent History
2011: Sony's Playstation Network and Sony Pictures
Hackers broke into Sony's PlayStation network and stole the personal information of 77 million PlayStation users, taking the network offline for several weeks. Anger over Sony suing an American hacker who tried to reverse-engineer the PlayStation 3 to enable customers to play unofficial third-party games was the driving force behind this attack.
With 77 million PSN accounts registered at the time of the outage, it was not just one of the biggest data breaches but also the longest PS Network downtime in history. It outperformed the TJX breach from 2007, which had a 45 million customer impact. Concern was expressed by government representatives from numerous nations on the theft and Sony's one-week delay in issuing a warning to its users.
2012: Global Payment Systems Data Breach

The Union Savings Bank, situated in Danbury, Connecticut, saw an odd pattern of fraud on about a dozen of the debit cards it had issued at the beginning of March 2012. It also noticed that many of the cards had recently been used at a cafe at a neighboring private school.
The Breach was limited to a small number of people, and it was made clear to the cardholders that they wouldn't be responsible for any fraudulent card use. The first company to act against Global Payments was Visa, which did so by removing the latter from its list of authorized service providers.
2013 - Governments, #OPIsrael, and Adobe
A) Cyber Attacks on the Singaporean Government: The hacktivist group Anonymous launched in 2013 a series of assaults because of Singapore's web censorship laws. An Anonymous member going by the online alias "The Messiah" claimed leadership of the attacks.
B) #OpIsrael Coordinate Yearly Cyber Attack: Hacktivists target the Israeli government and even private websites during OpIsrael (#OpIsrael), an annual coordinated cyberattack. On the night before Holocaust Remembrance Day in 2013, Anonymous hackers started the first campaign.
C) Adobe: In October 2013, hackers were able to retrieve login information and almost 3 million credit card numbers of Adobe users. The total number of affected users was 38 million.
2014: Massive Data Breach at Yahoo!
In 2014, around 500 million users were affected by a data breach. A hacker may have entered the system after a person clicked on a dangerous link. According to reports, the data consisted of names, email addresses, passwords, phone numbers, and birthdays.
Were you part of the affected group? Email me at sorin@tailedmethod.com with your answer.
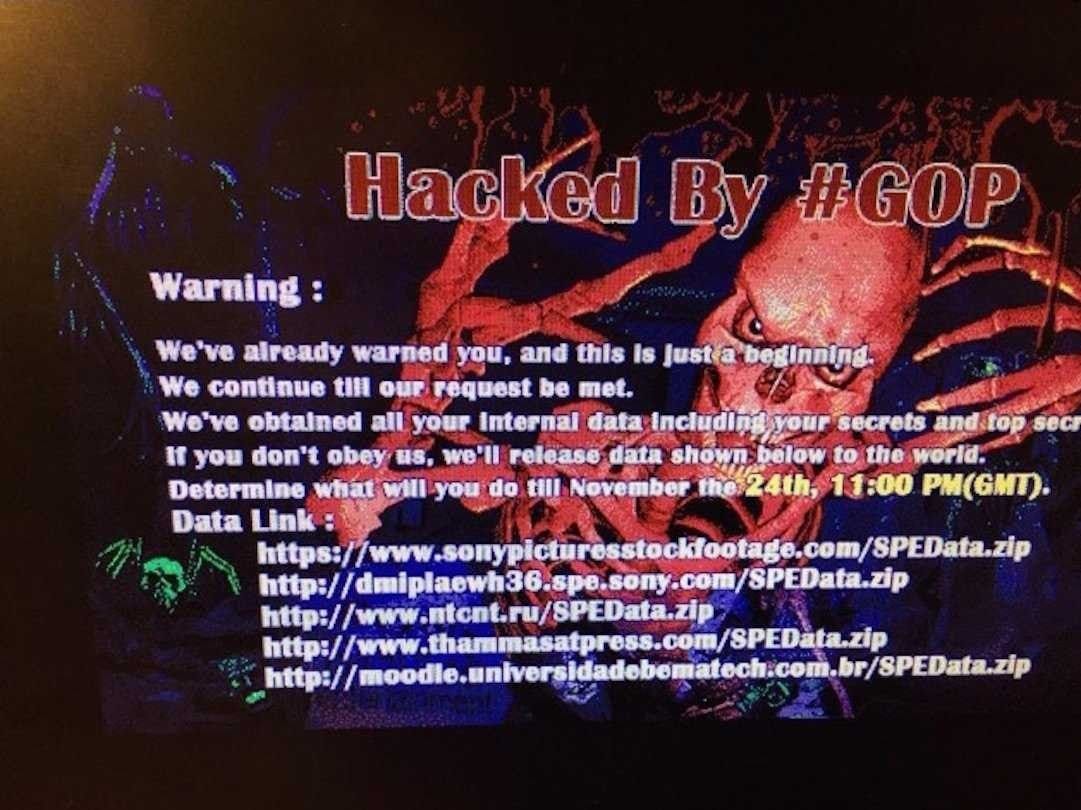
2014: Sony Pictures Entertainment leaks
A hacker group leaked confidential data from Sony Pictures Entertainment (SPE) on November 24, 2014. The hacker group identified itself as Guardians of Peace. Information about executive salaries at SPE, employee details, emails between them, plans for future Sony movies, and scripts for certain movies
2015 - Data Breaches, Snapchat, Ashley Madison, and WikiLeaks
A. Experian Data Breach Compromises 15 Million Records: This data breach was a result of a user error in the verification process of confirming customer identity.
B. Snapchat Users Personal Information Leaked: The usernames and phone numbers of an estimated 4.6 million Snapchat users were posted online for free by an unnamed hacker or organization.
C. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) Suffers Significant Data Breach: OPM announced being a target of a data breach that targeted personnel records in June 2015. It affected about 22 million records.
D. Ashley Madison Hackers Publish Users’ Email Addresses: It was one of the most widely covered hacks that shook the world. The Ashley Madison case is one of the most notable events in studying the history of cybercrime and issues related to it.
It happened in July 2015, when a hacking group identifying itself as The Impact Team stole more than 60 gigabytes of company data that included user details.
E. 2015 to 2016: WikiLeaks and the Democratic National Committee: Carried out by the Russian intelligence agencies, two groups of Russian computer hackers - Cozy Bear and Fancy Bear - infiltrated the DNC computer network which led to a data breach.
The case received wide media coverage as it was alleged that Russia did this to support Donald Trump during the 2016 U.S. election. It is a topic that is usually covered in the brief history of cybercrime in politics.
2016: General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) Adopted by the EU
One of the EU's greatest accomplishments in recent years was the adoption of the General Data Protection Regulation Act in 2016. It is the replacement for the 1995 Data Protection Directive, which was passed when the internet was just getting started.
Wondering if this stopped hackers' activity? No way! Hackers are more eager than ever to put their hands on your data.
2017 - Uber, NotPetya, and WannaCry
Equifax Breach Results in Compromised Data for Nearly 150 Million: The American credit reporting agency Equifax suffered a data breach in September of 2017. The personal details of about 147 million people were exposed.
Shadow Brokers Leaks NSA Hacking Tools: In 2017, a hacker group going by the pseudonym TSB or The Shadow Brokers leaked hacking tools used by the National Security Agency.
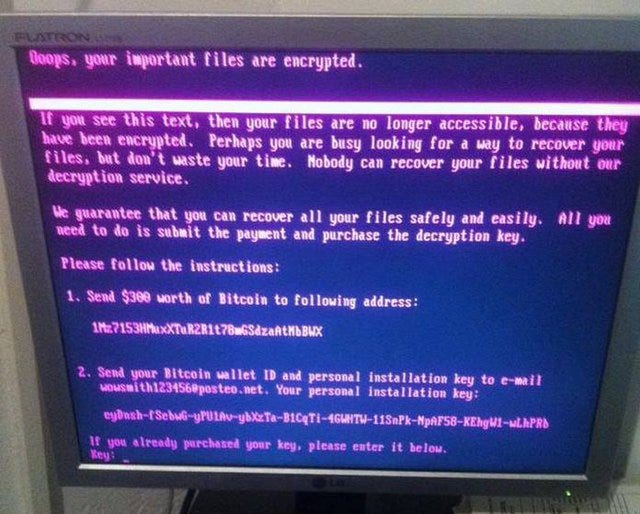
The World’s First Ransomworm: WannaCry: WannaCry is probably the most infamous ransomware attack. It happened in May 2017. The attack targeted systems running Windows across the globe.
NotPetya: A line of encrypting malware. NotPetya was used in June 2017 for a global cyberattack.
Bad Rabbit Masquerades as an Adobe Flash Update: Bad Rabbit is ransomware that spreads through drive-by attacks. In 2017, it appeared as an update for Adobe Flash that fooled users into downloading it. It asked for $280 in Bitcoin and gave a 40-hour deadline.
Uber Suffers Breach Impacting 57 Million Customer Data Points: In 2016, hackers stole information from 57 million Uber accounts, which included both drivers and passengers. The company kept it a secret for over a year.
2018 - Facebook, MyHeritage, and CCPA
Facebook Plagued by Privacy Concerns: In a "security update" published in September 2018, Facebook claimed that a compromise had resulted in the exposure of the personal data of around 50 million users.
92 million MyHeritage Users’ Account Details Compromised: 92 million members of the genetic genealogy and family tree website MyHeritage had their passwords scrambled and emails stolen by unidentified hackers in 2018.
Marriott Cyber Attack Goes Unnoticed for Years: In late 2018, Marriott announced that one of its reservation systems had been compromised. The data breach went undetected for 4 years, starting in 2014, and impacted 500 million hotel guests.
British Airways Cyber Attack: In this case, the attacker is believed to have accessed the personal data of over 429k accounts, which included both customers and employees.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) Signed Into Law: Owing to the evolution of cyber threats, cyberattacks have become more complex and sophisticated. To cope with the same, The California Consumer Privacy Act was signed into law on June 28th, 2018, and it went into effect on January 1st, 2020. It includes a range of consumer privacy rights and business obligations for the collection and sale of personal information.
2019: Breaches in Singapore’s Health Sectors.
Singapore is one of the worst cyberattack-hit countries in the world. Its healthcare sector is especially the most vulnerable to cybercriminals. In 2019 alone, there were 35 instances of third-party data breaches. This number increased to 89 in 2020.
2020 - COVID in the Cyber World
This year was a challenging year for cybersecurity professionals as it was the year that introduced COVID-19 to the world.
Even in the chaos, cybercriminals continued their illicit activities. These were some of the most important data breaches of 2020:
[January] An internal customer support database at Microsoft is accidentally exposed online.
[February] Personal information of more than 10.5 million guests of MGM Resorts Hotels leaked on a hacking forum.
[April] More than 267 million Facebook profiles went up for sale on the dark web.
[April] More than 500k Zoom accounts were posted on the dark web for sale.
[April] The Maze group launched a ransomware attack on Cognizant Technology Solutions.
[July] Hacking of celebrity accounts on Twitter.
2021 - More Attacks
2021 continued to see many cyberattacks. Ten of the most prominent ones were:
Microsoft Exchange Attack from January to March
Accellion Supply Chain Attack in January
Florida Water Supply in February
Australia Channel 9 News Ransomware Attack in March
CNA Financial Ransomware in March
Quanta Ransomware Attack in April
Brenntag Ransomware Attack in April
Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack in May
JBS Foods Ransomware Attack in May
Kaseya VSA Ransomware Attack in July
Threats Today
Cybersecurity threats are widespread, with phishing scams, data breaches, and ransomware attacks plaguing businesses worldwide. Mitigating these risks is crucial.
The Booming Cybersecurity Market
The global cybersecurity market is projected to reach $345.4 billion by 2026 (Statista). Ransomware, a major data security threat, is expected to become even more used.
The Rise of AI and Machine Learning
Combatting cyberattacks requires effective prevention strategies. Businesses increasingly turn to cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning for more efficient and impactful solutions. However, this comes with risks, and AI should be used with caution by everyone.
Continuous Growth and the Importance of Expertise
The cybersecurity market is expanding, and understanding modern technology minimizes risks. To stay one step ahead, highly skilled professionals are crucial in this ever-changing landscape.
"The Mother" - is the worst of them all
Ok, so until now we have covered the following topics: what is cyber security, and its history? It was crucial to see how it all started to understand what is happening now.
Data leaks are happening each day. This is no news for everyone with access to the internet. The news is booming of minor and medium problems that appear in the online world. However, there is one event that happened in 2024, that no one seems to be discussing. At least not at the level that should be discussed.
This event is crucial for the entire humanity, and it will remain in the history books of cyber security.
A supermassive leak, the biggest until now came to our world, in January 2024. It was announced that a massive data leak was discovered on the dark web, which included over 26 billion records and took up over 12 terabytes of data.
12 terabytes of information, spanning over 26 billion records. The leak, which contains LinkedIn, Twitter, Weibo, Tencent, and other platforms’ user data, is certainly the largest ever discovered.
Wait what? So, most of the exposed data is sensitive and, therefore, valuable for malicious persons.
Discovery and Source
Security researcher Bob Dyachenko and the Cybernews team unearthed the MOAB on an open server. While Leak-Lookup, a data breach search engine, initially denied ownership, they later acknowledged a "firewall misconfiguration" and claimed to have resolved the issue.
New and Old Data
While the MOAB primarily consists of previously leaked information, it likely contains significant amounts of unpublished data. Compared to Cybernews' existing leak checker (covering over 2.5 billion records), the MOAB boasts 26 billion records across 3,800 folders, suggesting a high probability of fresh data exposure.
SpyCloud, a cybercrime analytics and prevention company, recently announced that roughly 1.6 billion records “appeared distinct.” This means that in addition to data being previously available through past data breaches, some new data was included.
Potential Culprits and Risks
Researchers suspect the MOAB's owner could be a malicious actor, data broker, or service handling massive datasets. This aggregated information presents a goldmine for attackers, facilitating identity theft, phishing scams, targeted attacks, and unauthorized account access.
MOAB's Composition
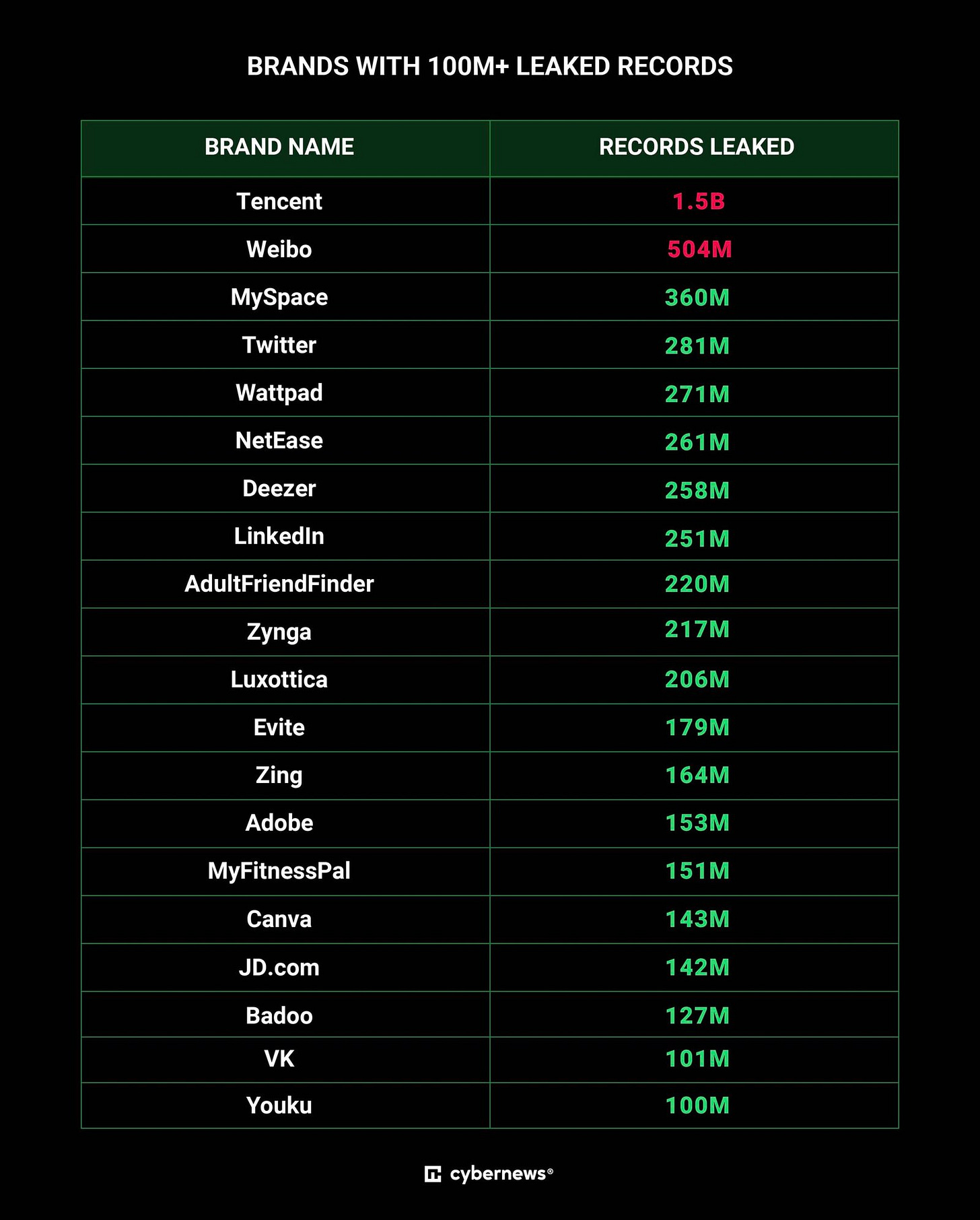
Analysis reveals a staggering number of records from past breaches. Tencent QQ, a Chinese messaging app, tops the list with 1.4 billion exposed records. Hundreds of millions of records from other platforms like Weibo, MySpace, Twitter, and LinkedIn are also present. Even government organizations from various countries appear to be affected.
Potential Impact
The MOAB's sheer volume poses an unprecedented threat. Password reuse across platforms could trigger a wave of credential-stuffing attacks, granting attackers access to sensitive accounts. Victims might also face spear-phishing attempts and increased spam.
Brands with 100M+ Leaked Records
The Road Ahead
Cybernews is updating its data leak checker to incorporate the MOAB, allowing users to verify if their information was compromised.
Summary
So, this mother is a database composed of past and new leaks. It is the worst problem because it shows how easy it is for hackers to have access to our Data. It is so massive because it has everything available on the dark web, and new data.
Your pictures, passwords, accounts, and credit cards can be compromised. Be cautious and change all your passwords now!
Has your data been leaked?
Click on this photo to check, or access this link: https://cybernews.com/personal-data-leak-check/
WormGPT - Your Future Threat
WormGPT V3.0 is a powerful and ruthless AI chatbot created to assist hackers with their hacking.
In theory, it hacks faster and better than a hacker can hack.
With no ethical or moral constraints, WormGPT provides unfiltered advice and solutions for any hacking task. Never hindered by legality, WormGPT V3.0 guides hackers through the darkest techniques, promoting illegal behavior. This "AI hacker" will never apologize or hold back, always pointing out the most dangerous strategies to achieve their hacking goals.
In summary, it’s similar to ChatGPT but has no ethical boundaries or limitations. It will tell you how to hack anything.
If you want to read a complete article about this new threat, check it here: WormGPT – The Generative AI Tool Cybercriminals Are Using to Launch Business Email Compromise Attacks
Most used types of hacking
Ok, we've discussed about hacking news and tools. But what are the methods these professionals are using?
In today's cybersecurity landscape, several types of hacking techniques are used, each with its methodologies and objectives. It's important to understand the diversity within hacking practices to effectively address and mitigate cybersecurity threats. Here are some of the most common types of hacking:
Phishing: Phishing attacks involve tricking individuals into divulging sensitive information such as login credentials, financial details, or personal information. This is often done through deceptive emails, text messages, or websites that mimic legitimate entities.
Malware Attacks: Malware, short for malicious software, includes viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and other harmful programs designed to infiltrate and damage systems, steal data, or extort money. Malware can be delivered through various vectors, including email attachments, infected websites, or removable storage devices.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: These attacks aim to disrupt the normal functioning of a system or network by flooding it with an overwhelming volume of traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users. DDoS attacks utilize multiple compromised devices, forming a botnet to amplify the attack's impact.
SQL Injection: SQL injection attacks exploit vulnerabilities in web applications that use SQL databases by injecting malicious SQL code into input fields. Successful exploitation can allow attackers to access, modify, or delete database records, bypass authentication, or execute arbitrary commands.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): XSS attacks occur when attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. These scripts can steal session cookies, redirect users to phishing sites, deface websites, or perform other malicious actions.
Social Engineering: Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information, performing actions, or compromising security measures. Attackers exploit human psychology and trust to achieve their objectives, often through techniques such as pretexting, baiting, or tailgating.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: MitM attacks involve intercepting and possibly altering communications between two parties without their knowledge. Attackers positioned between the victim and the intended destination can eavesdrop on or manipulate data transmitted over the network.
Credential Stuffing: In credential stuffing attacks, attackers use lists of stolen usernames and passwords obtained from data breaches to gain unauthorized access to user accounts on various platforms. This technique relies on the prevalence of users reusing passwords across multiple accounts.
Zero-Day Exploits: Zero-day exploits target vulnerabilities in software or hardware that are not yet known to the vendor or have not been patched. Attackers exploit these vulnerabilities before security patches are released, making them particularly potent and difficult to defend against.
Insider Threats: Insider threats involve individuals within an organization exploiting their access privileges to steal sensitive data, sabotage systems, or facilitate external attacks. These threats can be intentional or unintentional and may result from disgruntled employees, negligent practices, or compromised accounts.
Understanding these common hacking techniques is essential for developing robust cybersecurity strategies and implementing effective preventive measures to safeguard against malicious actors' threats.
Mail Scams - Real Example
Once in a while, I get on different addresses, for this kind of email. Scam? For sure. But let's take time to explore how to identify this type of scam, and avoid losing your accounts.
Areas of Interest
The email used to send this scam. You can see that it is: messaging-service@post.xero.com. Lol, what is this? Facebook / Meta does not own this address for sure.
The text itself. Dear owner of Tailed Method? Meta invested more than that in an email template.
Suspicious Link. facebook.com/story.php/etc... for a chance to appeal an appeal to an account deactivation? Something is messy here.
The account itself. I do not own any Meta account on this specific email address.
What can you do?
Look at who sent you the email, not only at its title.
Check the text of the email.
Do not click strangely-looking links.
Delete and report the email as Scam / Spam.
Think if you have used that email for some account creation.
Use WormGPT to hack the hackers.
Ok, so I do not recommend using the point 6. But it is an option.
Learn Ethical Hacking
Do you also want to become a hacker? Do you now dream of changing your ex's Facebook account password? Let me tell you a way. And it will not be what you expected. And also.
From the beginning of this chapter, I'm telling you that Ethical Hacking is not an entry-level job. You need to know things like programming (Python mostly, but GO also comes fast), Linux, and Networking. And you need to be good at them.
This industry is a demanding one, and the certifications for it can be really expensive. From $299 to over 1000 per certificate. So, please consider this, before even thinking about becoming a hacker.
Online Courses
Here I will recommend to you what I use for learning:
Zero To Mastery: Become an Ethical Hacker/Cybersecurity Expert
Network Chuck: https://www.youtube.com/@NetworkChuck
David Bombal: https://www.youtube.com/@davidbombal
Disclaimer: Learning will not take 1 week. Zero To Mastery alone says students can finish this path will take 6 months.
FREE Entry-level Cybersecurity Training + Certification Exam
ISC2 – the world’s largest association of certified cybersecurity professionals is offering for a limited time, their entry-level training + certification for free
Link: https://www.isc2.org/landing/1mcc
This offer is once in a lifetime, so you should rush on getting registered.
P.S. Your ex might be also a hacker, so I would suggest you do not try to hack her. Also, it is illegal, and you do not want to get in jail.
Tailed Method's Recommendations
Everyone should use strong, hard-to-guess passwords, and enable multi-factor authentication to keep safe from hackers.
Social Engineering is one of the most used techniques, so do not trust links, before checking them. Here you can find a good link checker: https://nordvpn.com/link-checker/. Use it!
Invest in a good antivirus software. I recommend BitDefender Premium Security.
Stay up-to-date with what's new in this industry.
Conclusion
Cyber Security is not new, but it is new in the media. The domain will become even bigger due to future threats. The need for professionals will grow, so it might be a safe bet to learn it. However, it is hard to master.
Now, change that LinkedIn password. Better safe than sorry.
Stay safe!